Understanding the causes of climate change and finding global solutions
Climate change is the single biggest challenge currently faced by humanity. Its effects directly or indirectly impact every area of life in all parts of the world, in ways both small and large.
From changes in indigenous flora and fauna to extreme weather events, from consumer choices to national legislation, from individual transportation to international industry, the consequences of man-made climate change are all around us. To slow, stop or even reverse climate change, we have to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere.
Decarbonization is the only way forward. The first step towards a carbon-neutral future is understanding the terminology, solutions and technologies necessary to achieve it. Green up your vocabulary and wise up to humanity’s greatest challenge with our decarbonization glossary.
A - C
-
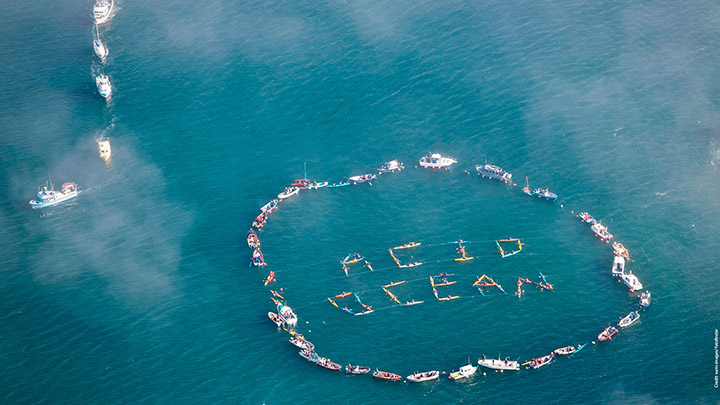
Acidification of the ocean
How is ocean acidification caused, how does it affect marine ecosystems. How can this change in seawater chemistry be avoided? CO2 emissions are key.
-

-
C - D
-
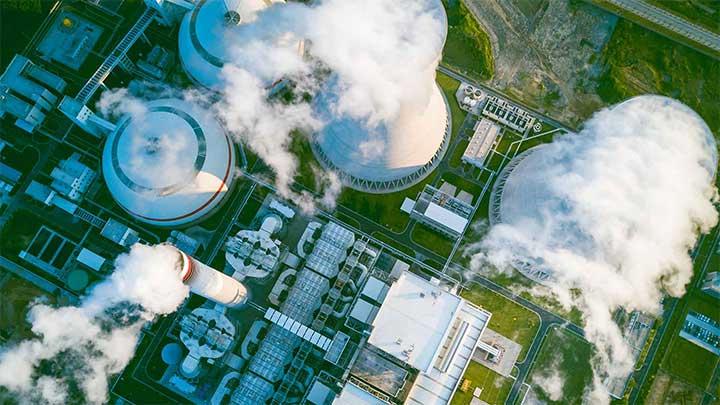

Carbon Capture and Storage
How does Carbon Capture and Storage work? Why is CCS Important to Energy Transition? What are the developing CCS technologies? Check our glossary.
-

Carbon dioxide (CO2)
What is carbon dioxide, where does carbon dioxide come from and how do CO2 emissions affect the earth? Our Decarbonization Glossary explains all.
-

Climate change
What is the definition of climate change, how does it impact the environment and what can we do to solve the climate crisis? Check our glossary.
-

Combined Heat and Power
What role does CHP play in energy transition? Why is CHP relevant to industry and heat supply? What challenges does CHP present?
-

Decarbonization
Decarbonization is central to climate policy. To reach environmental goals and damp the effects of global warming, reducing carbon emissions is vital.
E - F
-

Emission control
Emission control helps reduce the pollutants emitted by combustion engine exhaust. Why is it necessary and which emissions control systems are effective?
-

Energy transition
The global energy transition to renewable energy sources is a pressing issue for citizens, politics and industry alike, but how is the term defined?
-

Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels include some of the world’s most widely used energy sources. Our definition explains why these non-renewables contribute to climate change.
G - L
-

Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the only natural, fully renewable energy source that is constant, stable and does not fluctuate. So, what are the disadvantages?
-

Green fuels
How are green fuels produced from renewable energy and hydrogen and why are they relevant for the industry?
-

Greenhouse Gases
What different greenhouse gases are there? How do we reduce or transform greenhouse gases? What new technologies are being explored?
-
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon atoms. Burning them releases CO2, and uncombusted hydrocarbons also contribute to climate change.
-

-

Industrial Heat Pumps
Why are industrial heat pumps relevant to the industry? What are its challenges? What projects does MAN Energy Solutions have in progress?
M - R
-

Maritime Energy Transition
How can maritime shipping reduce its emissions? What are the challenges for the maritime energy transition? Our glossary explains.
-

Methane Slip
Why is methane slip specially relevant to the maritime industry? What are the challenges and what are the plans to reduce methane slip from engines? Find the answers in our glossary.
-

-

-

Power-to-X
What is Power-to-X? How does Power-to-X work? Why is Power-to-X important for the industry? What are the challenges?
S - U
-

SNG - Synthetic Natural Gas
What is the difference between SNG and other types of gas? Our glossary explains why SNG could be the carbon-neutral fuel of the future.
-
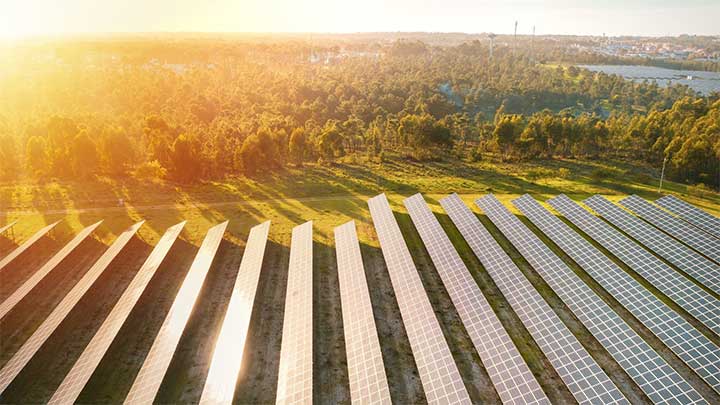

Solar Power
What role does solar power play in the energy transition? What are the challenges and disadvantages? How does solar thermal contribute to the energy transition?
-

Thermal energy
What is the definition of thermal energy, how does it relate to temperature, heat and cold and how can that specific type of kinetic energy be harnessed?
-

United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
What is the UNFCCC, how is it related to the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement? And are these climate agreements successful?
W
-
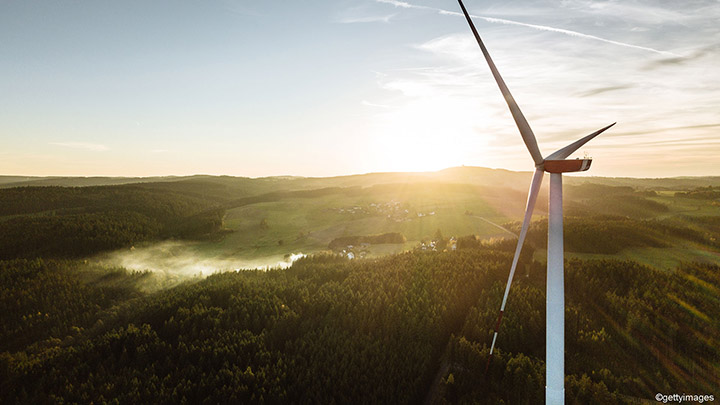

Wind power
Wind power has a long history, but today it is mainly used to generate renewable energy with turbines. Find out more about the advantages and disadvantages.
MAN Energy Solutions is now Everllence.
We have adopted a new brand name and moved to a new domain: www.everllence.com. This page will also be relocated there shortly. We are working on shifting all pages to www.everllence.com.
